- Towards AGI
- Posts
- Can Quantum Computing Surpass the AI Revolution?
Can Quantum Computing Surpass the AI Revolution?
Quantum vs. AI
Here is what’s new in the AI world.
AI news: Quantum's Ambition: Bigger Than AI?
Hot Tea: The Automated Game Tester is Coming
Open AI: The Open-Source AI Advantage
OpenAI: OpenAI CFO's Defense of Long-Term Potential
How Quantum Could Be the Foundation for a New AI
You've probably heard the hype about quantum computing, but you might find it hard to grasp. That's because it's famously difficult to explain accurately in a way that's also easy to understand.
At its heart, quantum mechanics deals with tiny particles behaving in bizarre ways. This strange behavior is the key to a potential scientific superpower. But its sheer complexity is a big reason why it hasn't become a household name like its flashy cousin, Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Think of it this way: you tend to see quantum as hardware (like sensors and computers), while AI is the software that needs hardware to run.
Now, imagine combining them. You might get a technology more powerful than anything we've ever created. But that "might" is doing a lot of work, experts warn.
The potential is there, but the jury is still out. Initial experiments are promising, but they show you'd need much more powerful quantum computers and more research to truly make it work.
The Hype and The Money
Both fields are swimming in money and hype. The quantum sector could be worth nearly $100 billion by 2035. But AI is forecast to be worth trillions.
Just like with AI, you have to be wary of bubbles. As one analyst jokes, he used to think quantum was the most-hyped tech until the AI craze took over.
The Quantum Problem: It's Fragile

Source - MIT
You're likely familiar with AI "hallucinations", where it makes up false information. Quantum has a different, physical problem: errors.
The state the quantum particles operate in is incredibly fragile. The slightest change in light or noise can disrupt them. It's so tricky that some, like Elon Musk, have even suggested they'd run best on the moon!
What Does a Quantum Computer Look Like?
Forget the laptop on your desk. Quantum computers don't look like any machine you own. They are currently massive lab-bound structures, often with a strange, jellyfish-like shape.
They need extremely cold temperatures and lasers to function. You won't be putting one in your pocket anytime soon.
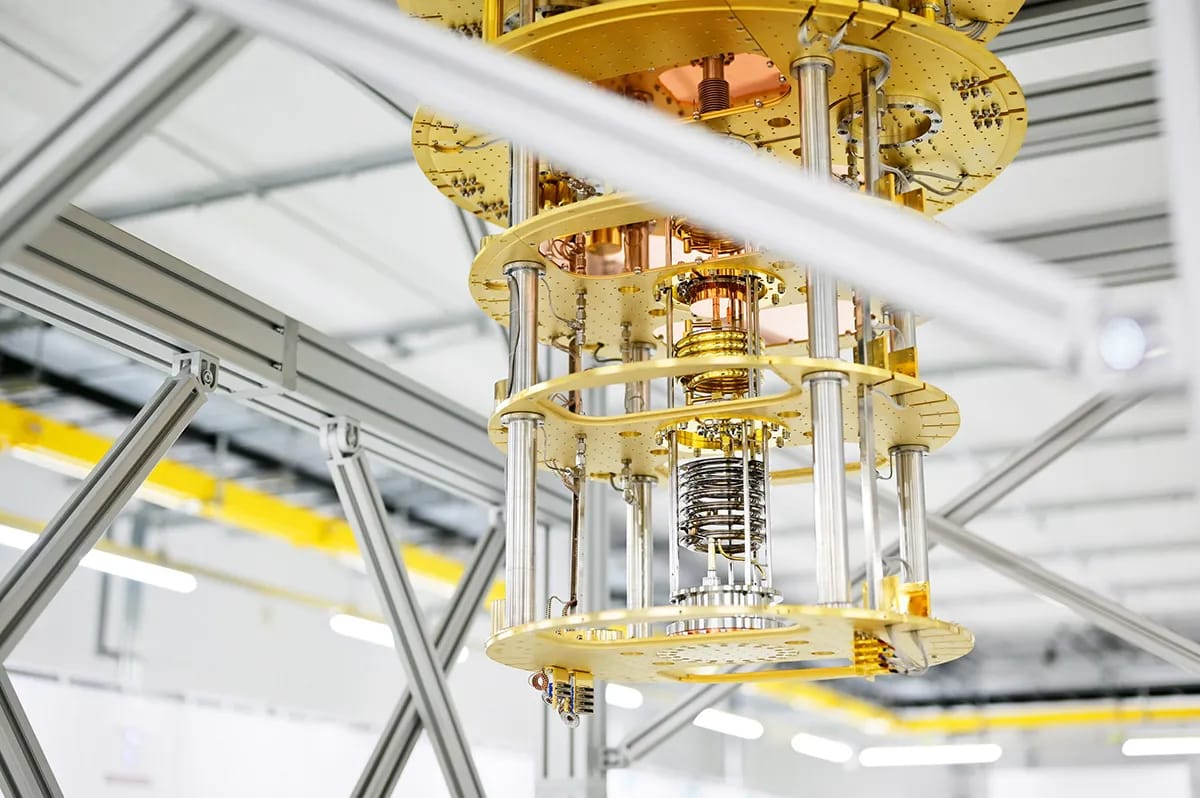
They can also be a bit bling. Researchers found that using synthetic diamonds helps them operate closer to room temperature. The luxury jeweler De Beers even has a subsidiary working on quantum-grade diamonds with Amazon.
So, What Could You Actually Do With It?
Despite being in its infancy, experts make bold claims about how quantum computing will touch almost every part of your life. They say it could be bigger than AI.
The core promise is speed. A calculation that would take today's best supercomputer longer than the age of the universe could be done by a quantum computer in seconds.
This could revolutionize fields like:
Healthcare: It could effortlessly sift through endless molecular combinations to discover new, personalized drugs tailor-made for your body, a process that currently takes years.
Brain Scans: Quantum sensors are already being used in portable brain scanners that can study children's brains without requiring them to stay perfectly still, offering new insights into conditions like epilepsy.
Navigation: Imagine a "quantum compass" that works anywhere, underground, underwater, without being blocked or jammed like GPS. This could secure everything from financial transactions to defense systems.
Energy & Transport: The power grid could use it to prevent blackouts, and airlines could use it to perfectly balance cargo, saving thousands of kilos of fuel.
The Dark Side: The Secrets You Want to Keep
There's a catch that keeps security experts up at night. The power that could design new medicines for you could also be used to break the encryption that protects all your digital secrets.
Nations are already suspected of stealing encrypted data today, with a plan to "harvest now, decrypt later", waiting for a powerful enough quantum computer to crack it open.

The day this happens is sometimes called "Q-Day," and some estimates place it around 2030.
Companies like Apple and Signal are already rolling out new, "quantum-resistant" encryption, but it can't protect the data that has already been stolen and stockpiled.
It's credible that almost all of your personal data may have already been compromised in state-sponsored attacks, waiting for the day it can be unlocked and examined.
While quantum computing captures our imagination with its futuristic potential, artificial intelligence is already transforming your business and daily life. While researchers work to stabilize quantum particles, AI algorithms are already optimizing your supply chains, personalizing customer experiences, and detecting fraud in real-time.
The truth is: quantum computing remains a spectacular laboratory experiment, while AI is your ready-to-deploy competitive advantage. You don't need to wait for quantum's uncertain timeline to start leveraging transformative technology.
Journey Towards AGI
Research and advisory firm guiding industry and their partners to meaningful, high-ROI change on the journey to Artificial General Intelligence.
Know Your Inference Maximising GenAI impact on performance and Efficiency. | Model Context Protocol Connect AI assistants to all enterprise data sources through a single interface. |
Square Enix: 70% QA Automation via AI by 2027
Square Enix has announced an ambitious goal to use generative AI to automate 70% of its quality assurance (QA) and debugging tasks in game development by the end of 2027.
This target was revealed in the company's recent financial report and is part of a broader strategy to integrate AI and create more stable development foundations.
To achieve this, Square Enix has begun a joint research project with the University of Tokyo's Matsuo Laboratory, aiming to use AI to make game development more efficient and gain a competitive edge. The company has also held internal contests to generate AI-based project ideas.
This push for AI adoption follows a January 2024 statement from Square Enix president Takashi Kiryu, who promised the company would be "aggressive" in applying AI and other new technologies.
However, this stance exists alongside a more cautious industry movement concerning AI.
Just this week, Square Enix joined other major Japanese studios like Bandai Namco and Kadokawa (owner of FromSoftware) in a formal request, submitted through an anti-piracy group, demanding that OpenAI stop using their content to train its AI models like Sora 2.
The group alleges that the AI's outputs closely resemble Japanese copyrighted works, which may constitute infringement.
Furthermore, not all creators within Square Enix's sphere are embracing the technology. In a recent interview, Nobuo Uematsu, the legendary composer for the Final Fantasy series, stated that he has never used AI for music and probably never will.
He expressed that the human element, the personal background of the creator, and the imperfect, unique fluctuations in a performance, are what make music rewarding to create and satisfying to listen to.
Why Pinterest Loves Open-Source AI
Despite a disappointing financial forecast that caused its stock to drop, Pinterest is betting on open-source AI to power its future growth while keeping costs low.
The company, which helps users discover products and ideas, uses AI for many features, including personalized recommendations, image-based search, and its new shopping assistant.
However, investors are concerned about future revenue, especially after Pinterest predicted a weaker-than-expected holiday season, partly blaming the impact of Trump's tariffs.
In response to these concerns, CEO Bill Ready highlighted a strategic advantage: using open-source AI models.
He explained that Pinterest regularly tests leading proprietary AI models against open-source alternatives and has found that fine-tuned open-source models deliver comparable performance for its specific visual AI needs at a fraction of the cost.
Ready stated that using these open-source models leads to an "order of magnitude reduction in cost" while maintaining similar quality. This allows the company to control expenses as it expands its AI features.
Regarding the future of "agentic commerce", where AI acts autonomously to make purchases, Ready said Pinterest is taking a wait-and-see approach.
The company already has a "push-button" buying feature through its Amazon partnership and will gauge if users want AI to take that final step for them.
For now, Pinterest's focus is on guiding users through their shopping journey. Its new AI-powered Pinterest Assistant, for example, acts as a personalized style advisor that understands a user's tastes based on their saved pins and boards.
The company is also rolling out AI-curated boards that blend human expertise with artificial intelligence to offer personalized recommendations.
This is the power of AI when it's fueled by trustworthy, well-organized data. Pinterest's Assistant can only be so perceptive because the data from your pins and boards creates a rich, reliable picture of your style.
For any business looking to deploy AI that truly understands its customers, this is the foundational principle.
DataManagement.AI provides this essential data layer, ensuring your AI initiatives, from personalized shopping assistants to curated recommendations, are built on a foundation of accurate, unified, and contextual data, not guesswork.
OpenAI CFO on Balancing Bubble Fears with Necessary Optimism
OpenAI's Chief Financial Officer, Sarah Friar, believes that the public and the market are too focused on fears of an AI bubble and should instead be more excited about the technology's transformative potential.
Speaking at a tech conference, Friar argued that people aren't enthusiastic enough about the practical benefits AI can offer individuals and that the industry should "keep running at it."
This perspective comes amid growing scrutiny over the massive spending by tech companies on AI infrastructure, with OpenAI itself planning to invest over $1.4 trillion in data centers and chips, despite not yet being profitable.
A significant portion of this spending involves major deals with chipmakers like Nvidia. These agreements have been criticized as "circular financing," where a company like Nvidia invests in OpenAI, which then uses that money to buy Nvidia's chips.
However, Friar rejected this characterization, stating that the industry is simply building the necessary computational infrastructure and that OpenAI has worked to diversify its supply chain.
To fund its ambitious plans, OpenAI is exploring a wide range of financing options, including banks and private equity.
Friar also suggested a potential role for the U.S. government to act as a financial "backstop" to guarantee this funding, though an OpenAI spokesperson later clarified she was speaking broadly about the industry and that there are no immediate plans to seek such federal support.
Despite the need for vast capital, Friar confirmed that an Initial Public Offering (IPO) is not in the company's current plans, stating, "IPO is not on the cards right now."
This highlights a critical challenge for frontier tech companies: securing the massive, long-term capital required for R&D without sacrificing strategic control through a premature IPO.
This is precisely the complex financial and operational landscape that TowardsMCP is built to navigate. We provide the strategic capital and operational expertise that allows visionary companies to scale their ambitions without being forced onto the public markets before they're ready.
Your opinion matters!
Hope you loved reading our piece of newsletter as much as we had fun writing it.
Share your experience and feedback with us below ‘cause we take your critique very critically.
How's your experience? |
Thank you for reading
-Shen & Towards AGI team