- Towards AGI
- Posts
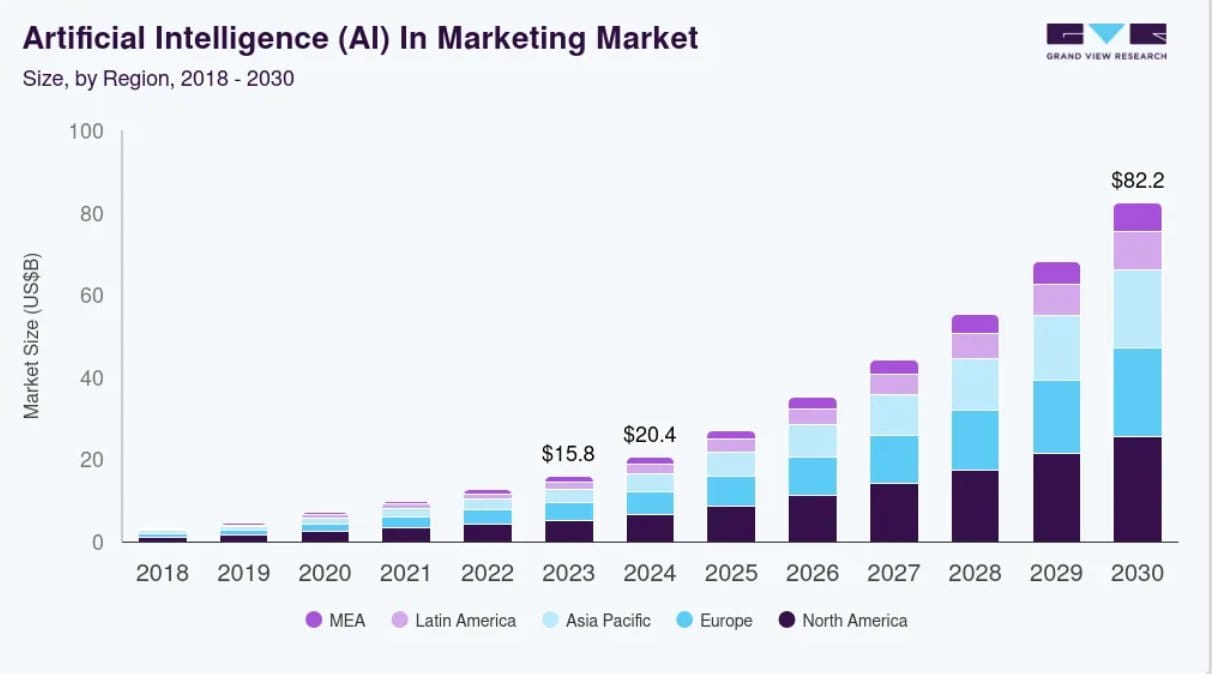
- AI Tools That Are Making Market Research More Agile
AI Tools That Are Making Market Research More Agile
Death of the Old Survey?
Here is what’s new in the AI world.
AI news: The AI Tools Every Market Researcher Needs to Know
Hot Tea: Use SAP's Generative AI to Future-Proof Your Business
Open AI: China is Now the Top Contributor
OpenAI: The Next Phase of AI: 220 Million Paying Users by 2030?

Is AI the Future of Market Research? The Tools Making It Happen
You know that traditional custom market research is notoriously slow and expensive, often forcing you to make critical strategic decisions without timely insights. Generative AI is now poised to transform this, fundamentally changing how you collect and analyze consumer data.
This shift is centered on two powerful new tools that act as proxies for people: the synthetic persona and the digital twin.
By using data to simulate human responses, these tools allow you to conduct research and experiments without the time, cost, and participant burden of traditional methods. They move you beyond the basic "oracle" approach of asking a raw question to a large language model (LLM) and hoping for a useful answer.
The Synthetic Persona: Understanding Your Segments
To use a synthetic persona, you provide an AI model with demographic, psychographic, or behavioral information about a customer segment. The LLM then answers questions as if it were that type of person. You can use this in two main ways:
The Top-Down Approach: You ask the composite persona for a single, "best" answer for the entire segment, like its average willingness to pay. Think of this as an AI super-agent for your segment.
The Bottom-Up Approach: You create a whole population of simulated consumers, known as a "silicon sample." You then ask this group questions and aggregate their individually varied answers, much like you would with a traditional survey.
You may find yourself more comfortable with the bottom-up approach because its variability feels closer to traditional research. However, it's still an open question which method works better for specific use cases.
The Digital Twin: Modeling Your Individual Customers
If you want to go beyond composite segments and capture the true heterogeneity of your market, you can use digital twins. If your company has detailed, individual-level data on customers from past interactions or surveys, you can use it to create a digital twin of each person.
These twins can then participate in virtual surveys and experiments.
Ambitious work in this area, like the Digital Twins Initiative at Columbia Business School, has shown both promise and limitations. Their research found that digital twins replicated human responses with 88% relative accuracy in a test-retest benchmark.
However, they only replicated about half of the experimental effects found in well-known behavioral studies.
A meta-analysis of 19 studies highlighted where digital twins show the most potential for you:
Strengths: Questions about social interactions (e.g., fairness in pricing) and human-technology interactions.
Limitations: Capturing diverse political opinions, avoiding socially desirable answers, and overcoming inherent "pro-human" and "pro-technology" biases.
When compared to synthetic personas, digital twins were better at capturing variations across people but were tied with personas (at 75% accuracy) in predicting exact answers. The conclusion for now is that digital twins show promise but are not yet fully "ready for prime time."
A critical challenge you will face is judging the quality of this synthetic data. You need to decide what to measure:
Accuracy: How close each synthetic response is to its human counterpart.
Correlation: How well variations among synthetic responses reflect variations among human responses.
Without individual-level data, you must rely on comparing averages and overall variations.
Your 8-Step Plan for Getting Started
While traditional research remains primary, now is the time for you to start experimenting.
Here is your step-by-step guide:
Determine Your Use Case: Precisely define what you need. Are you seeking a single estimate from a segment, or do you need to understand differential feature valuations?
Identify Your Target Consumer: Decide if you need the composite view of a segment (use a synthetic persona) or nuanced feedback from a specific set of consumers (consider digital twins).
Gather Calibration Data: This is often the limiting factor. Use your proprietary data for digital twins, or rely on aggregate/public data for synthetic personas.
Set Clear Performance Metrics: Before you begin, commit to your metrics (e.g., accuracy, correlation) to avoid cherry-picking results later.
Run a Small Test: Conduct a representative test with a sample of real human participants to establish a "ground truth" for comparison.
Evaluate Performance: Compare your synthetic data against your ground truth, using simple benchmarks to contextualize the cost-performance tradeoff.
Decide Whether to Scale: Based on your cost-benefit analysis, determine if integrating synthetic data into your research pipeline is worthwhile.
Ensure Ongoing Validity: Periodically test your twins or personas against real human data to keep your models accurate and up-to-date.
These tools may not be perfect yet, but they will soon revolutionize marketing. To stay ahead, you must begin experimenting with and investing in them now.
Driving Tangible Business Value with SAP's Generative AI
Corporate investment in generative AI is experiencing significant growth, with 80% of companies reporting an increase in funding compared to the previous year.
This trend is driven by clear, measurable returns; organizations focusing on generative AI have seen an average productivity improvement of 7.8% and a 6.7% boost in customer engagement and satisfaction.
The potential is even more pronounced when generative AI is implemented at scale, particularly for large-scale SAP transformation projects. SAP's integrated generative AI capabilities promise to accelerate the delivery lifecycle, enhance the time-to-value, and significantly improve the business user experience.
This technology facilitates continuous transformation across critical functions such as finance, supply chain, human resources, and sales.
For large SAP projects, the value of generative AI is concentrated in two key areas:
Optimizing the Delivery Lifecycle: A holistic approach integrates advanced AI into the software development process, revolutionizing how SAP applications are designed, developed, and maintained. This creates a competitive advantage by speeding up project timelines.
Enhancing Business User Experience and Productivity: Generative AI is not a standalone tool but an intelligence layer natively infused into business applications. This represents a disruptive shift in how businesses operate, make decisions, and optimize their core processes.
To harness this potential, a structured methodology has been developed that injects generative AI accelerators into the SAP software lifecycle. This approach is tailored to the four main types of SAP transformations:
Global transformations (Greenfield)
Brownfield and mixed migrations
Global rollouts
Single line-of-business implementations (e.g., SAP SuccessFactors)
Based on a detailed analysis of typical project phases, it is estimated that generative AI can positively impact 30-35% of project tasks, which account for 60-70% of the total project effort. This demonstrates its substantial role in driving efficiency and creating greater business value.
In the Open-Source AI Arena, China is Now the Top Contributor
A recent study from MIT and Hugging Face reveals that China has surpassed the United States to become the leading source for open-source AI models worldwide.
Over the past year, Chinese-developed models accounted for 17.1% of all global downloads, edging out the U.S. share of 15.8%. Key contributors to this lead include models from DeepSeek and Alibaba's Qwen.

These open-source models, which are free for developers to use, modify, and build upon, are crucial for accelerating innovation and product development globally. Their widespread adoption is actively shaping the trajectory of AI technology.
This milestone was highlighted by Ni Guangnan, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, at a recent developers' conference in Beijing.
China is now the world's largest provider of open-source large models.
This development aligns with the strategic direction outlined in China's 15th Five-Year Plan (2026-2030), which advocates for a higher level of opening up and international cooperation.
The expansion of China's influence is further evidenced by the rapid growth of its open-source communities overseas.
Ni cited a U.S. report indicating that a significant majority, 80% of American AI startups, now utilize Chinese open-source models.
He emphasized that China's open-source ecosystem is built on principles of inclusiveness and global collaboration, which helps pool international talent, foster technological exchange, and inject fresh momentum into global innovation.

Can ChatGPT Reach 220 Million Paying Users? OpenAI Is Betting On It.
The AI giant OpenAI has projected that at least 220 million weekly ChatGPT users will pay for a subscription by 2030.
This forecast estimates that 8.5% of an estimated 2.6 billion weekly users will subscribe to the chatbot, potentially positioning ChatGPT among the world's largest subscription businesses.
The report indicates that as of July, approximately 35 million users - representing about 5% of ChatGPT's weekly active user base- were paying for either "Plus" or "Pro" subscription plans priced at $20 and $200 per month, respectively.
While OpenAI's annualized revenue run rate is expected to reach approximately $20 billion by the end of this year, the company is also experiencing mounting losses.
It was also previously reported that OpenAI generated around $4.3 billion in revenue during the first half of 2025, representing a 16% increase over its total revenue for all of last year.
However, the company also burned through $2.5 billion, largely due to research and development costs for AI development and ChatGPT operations.
OpenAI anticipates that approximately 20% of its future revenue will come from new products, including shopping- and advertising-driven features.
This week, the company introduced a personal shopping assistant for ChatGPT, a move that could potentially lead to monetization through advertising or commission-based sales. Reuters noted that it could not immediately verify the report, and OpenAI did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Journey Towards AGI
Research and advisory firm guiding industry and their partners to meaningful, high-ROI change on the journey to Artificial General Intelligence.
Know Your Inference Maximising GenAI impact on performance and Efficiency. | Model Context Protocol Connect AI assistants to all enterprise data sources through a single interface. |
Your opinion matters!
Hope you loved reading our piece of newsletter as much as we had fun writing it.
Share your experience and feedback with us below ‘cause we take your critique very critically.
How's your experience? |
Thank you for reading
-Shen & Towards AGI team